Why agricultural compounds are used
Farmers and growers use agricultural compounds to help protect the food supply and to maximise the quantity and quality of the food they grow.
Agricultural compounds include agricultural chemicals (such as herbicides and other pesticides) and veterinary medicines, which are used to make sure crops and animals are healthy and to control pests. Using agricultural compounds helps to:
- keep crops and animals healthy
- manage outbreaks of pests and diseases
- increase the reliability of food production, which reduces the cost of many foods (because the crops and animals can produce more when there are fewer pests and diseases).
Agricultural compounds and food
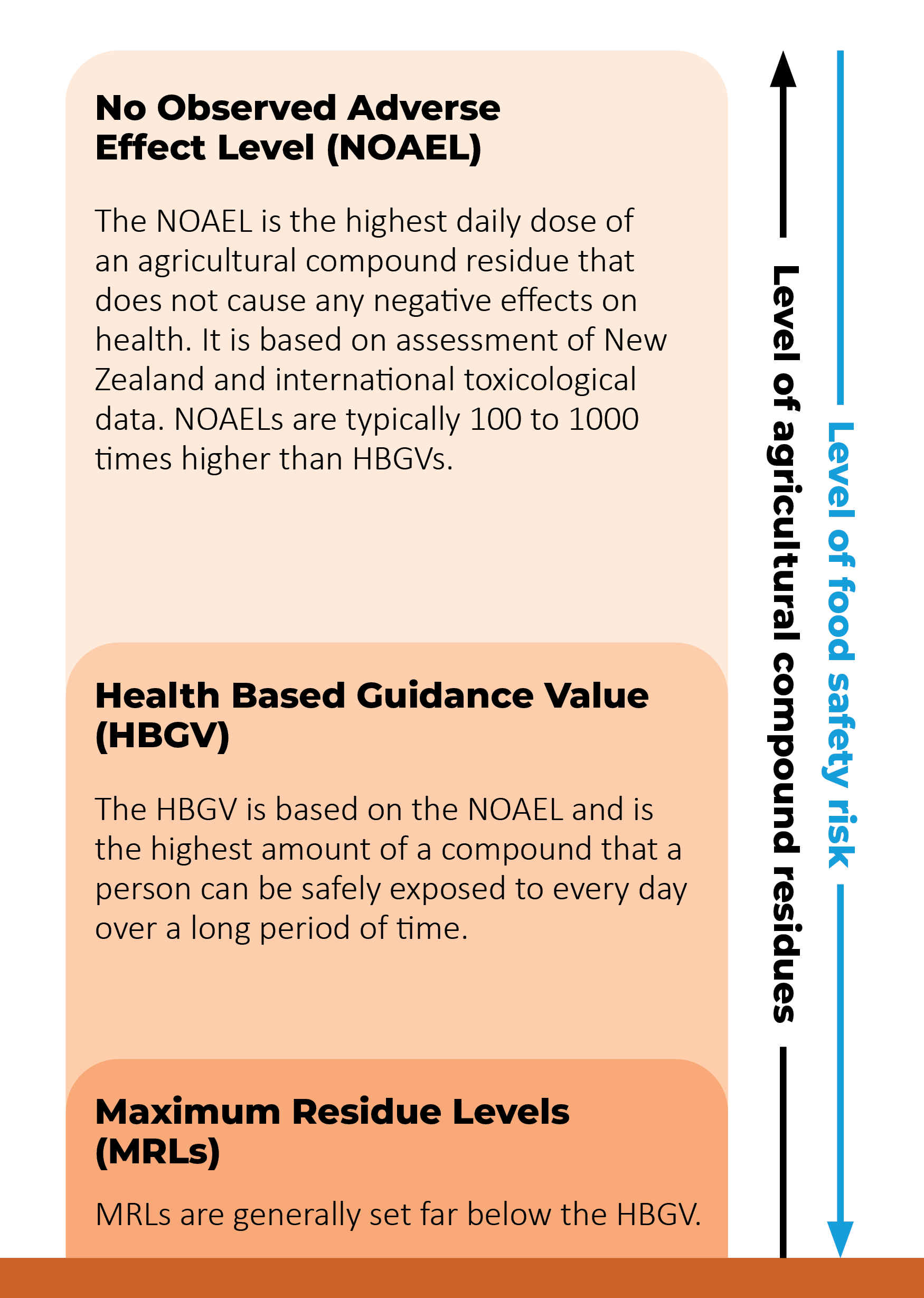
Agricultural compound residues in food are managed through maximum residue levels (MRLs). MRLs set the largest amount of the residue that is allowed in food.
Find out more about MRLs for agricultural compounds
MRLs are not often exceeded, and when they are, this is rarely a food safety concern. This is because all MRLs are set well below both international and New Zealand safe exposure limits.
If a residue found in food is assessed to be a food safety risk to consumers, we will take appropriate action. Warranted officers will follow up with suppliers to determine what happened and which corrective actions are needed. If there is a food safety risk, food can be recalled, and food production can be suspended.
Read more about how we enforce the Food Act 2014
Are agricultural compounds safe?
Low levels of agricultural compound residues can remain in food products (like fruit, vegetables, and meat). In New Zealand, residues are well within safe levels.
The Ministry for Primary Industries (MPI) follows internationally agreed protocols to set MRLs at levels that are well below what could harm somebody's health. This is because we set MRLs to ensure that good agricultural practice is being followed, rather than to the highest level allowed by food safety limits.